Lognormal Distributions in R
- 1 Table of Lognormal Distribution Functions in R
- 2 Plot of Lognormal Distributions in R
- 3 Examples for Setting Parameters for Lognormal Distributions in R
- 4 rlnorm(): Random Sampling from Lognormal Distributions in R
- 5 dlnorm(): Probability Density Function for Lognormal Distributions in R
- 6 plnorm(): Cumulative Distribution Function for Lognormal Distributions in R
- 7 qlnorm(): Derive Quantile for Lognormal Distributions in R
Here, we discuss lognormal distribution functions in R, plots, parameter setting, random sampling, density, cumulative distribution and quantiles.
The lognormal distribution with parameters \(\tt{meanlog}=\mu\), and \(\tt{sdlog}=\sigma\) has probability density function (pdf) formula as:
\[f(x)=\frac 1 {x\sigma\sqrt{2\pi}}\ e^{-{\frac {1}{2}}\left({\frac {\ln(x)-\mu }{\sigma }}\right)^{2}},\] for \(x \in (0, +\infty)\),
where \(\mu \in \mathbb {R}\), and \(\sigma>0\).
\(e\) is \(\tt{Euler's\;number}\) with \(e \approx 2.71828\), and \(\pi\approx 3.14159\).
The mean is \(e^{\left(\mu+\frac{\sigma^2}{2}\right)}\), and variance is \(e^{(2\mu+\sigma^2)}*[e^{\sigma^2}-1]\).
Note: If \(X \sim\tt{Lognorm} (\mu, \sigma)\), then \(\tt{\ln(X)} \sim \tt{Normal} (\mu, \sigma)\); or if \(X \sim \tt{Normal} (\mu, \sigma)\), then \(\tt{\exp(X)} \sim\tt{Lognorm} (\mu, \sigma)\).
See also probability distributions and plots and charts.
1 Table of Lognormal Distribution Functions in R
The table below shows the functions for lognormal distributions in R.
| Function | Usage |
| rlnorm(n, meanlog=0, sdlog=1) | Simulate a random sample with \(n\) observations |
| dlnorm(x, meanlog=0, sdlog=1) | Calculate the probability density at the point \(x\) |
| plnorm(q, meanlog=0, sdlog=1) | Calculate the cumulative distribution at the point \(q\) |
| qlnorm(p, meanlog=0, sdlog=1) | Calculate the quantile value associated with \(p\) |
2 Plot of Lognormal Distributions in R
Single distribution:
Below is a plot of the lognormal distribution function with \(\tt{meanlog}=2\) and \(\tt{sdlog}=0.6\).
x = seq(0, 35, 1/1000); y = dlnorm(x, 2, 0.6)
plot(x, y, type = "l",
xlim = c(0, 35), ylim = c(0, max(y)),
main = "Probability Density Function of
Lognormal Distribution (2, 0.6)",
xlab = "x", ylab = "Density",
lwd = 2, col = "blue")
# Add legend
legend("topright", "meanlog = 2, sdlog = 0.6",
lwd = 2,
col = "blue",
bty = "n")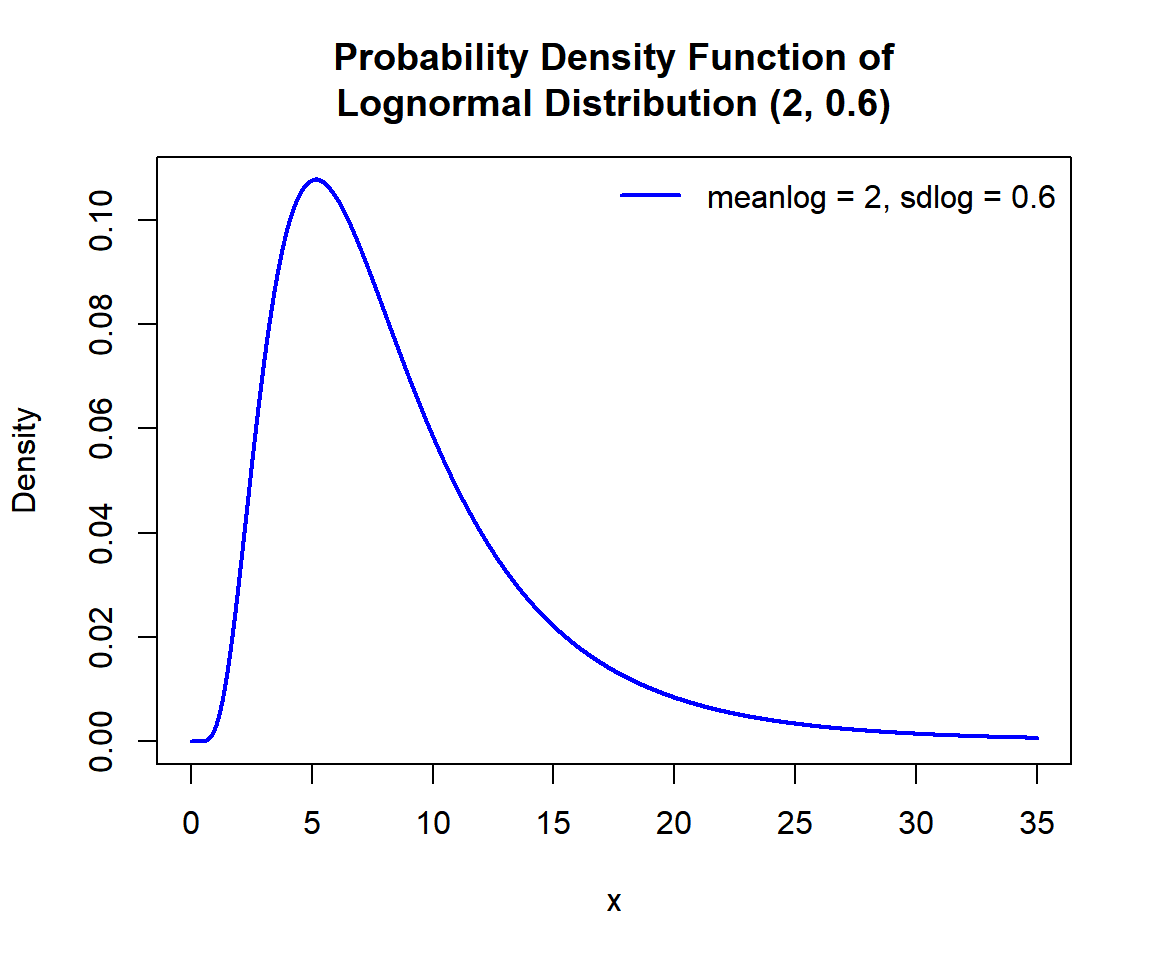
Probability Density Function (PDF) of a Lognormal Distribution in R
Multiple distributions:
Below is a plot of multiple lognormal distribution functions in one graph.
x1 = seq(0, 10, 1/1000); y1 = dlnorm(x1, 0, 1)
x2 = seq(0, 10, 1/1000); y2 = dlnorm(x2, 0.5, 0.75)
x3 = seq(0, 10, 1/1000); y3 = dlnorm(x3, -0.25, 1.2)
plot(x1, y1, type = "l",
xlim = c(0, 10), ylim = range(c(y1, y2, y3)),
main = "Probability Density Functions of Lognormal Distributions",
xlab = "x", ylab = "Density",
lwd = 2, col = "blue")
points(x2, y2, type = "l", lwd = 2, col = "red")
points(x3, y3, type = "l", lwd = 2, col = "green")
# Add legend
legend("topright", c("meanlog = 0, sdlog = 1",
"meanlog = 0.5, sdlog = 0.75",
"meanlog = -0.25, sdlog = 1.2"),
lwd = c(2, 2, 2),
col = c("blue", "red", "green"),
bty = "n")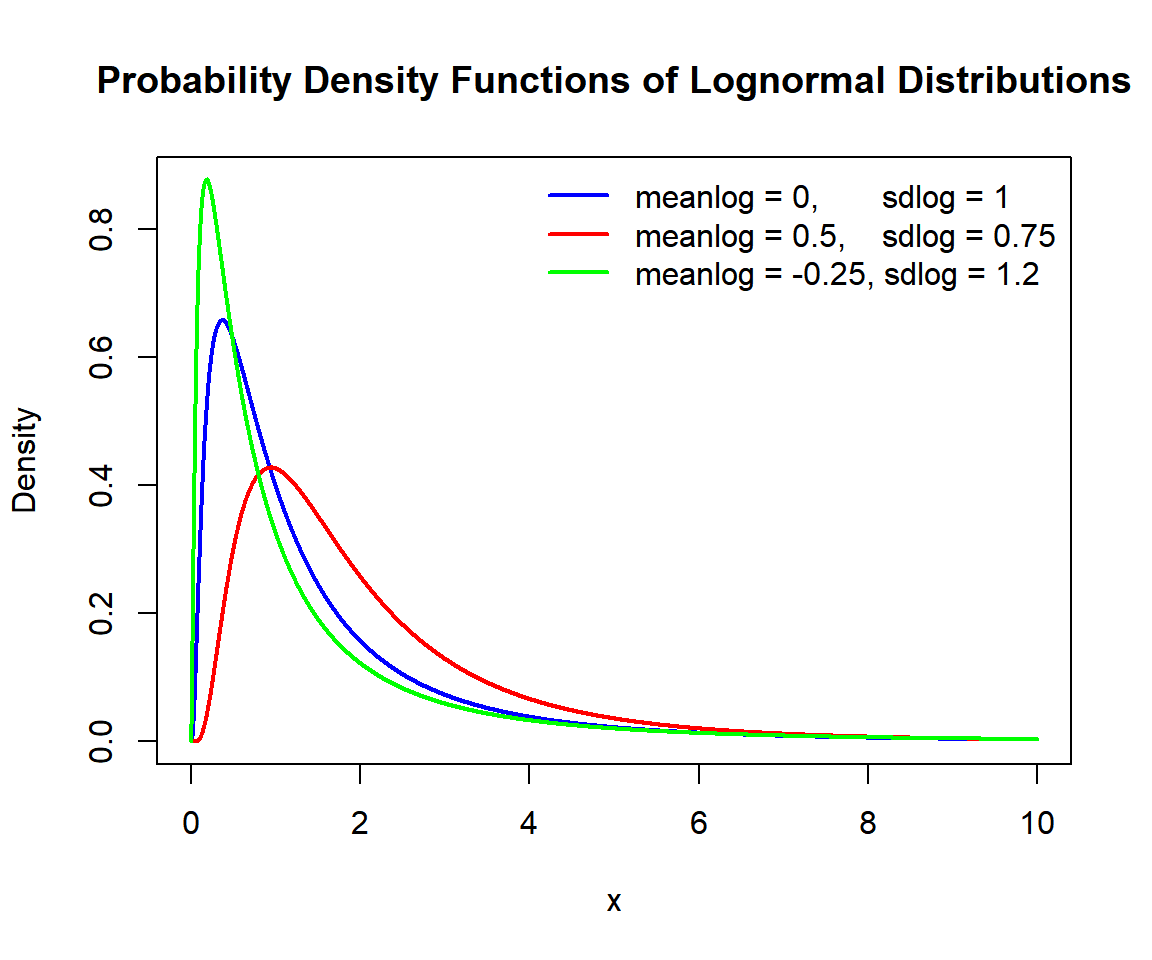
Probability Density Functions (PDFs) of Lognormal Distributions in R
3 Examples for Setting Parameters for Lognormal Distributions in R
In the lognormal distribution functions, parameters are pre-specified as \(\tt{meanlog}=0\) and \(\tt{sdlog}=1\), hence they do not need to be specified, unless they are to be set to different values.
For example, for dlnorm(), the following are the
same:
# The order of 0 and 1 matters here as the parameter names are not used.
# The first number 0 is meanlog, and 1 is sdlog.
dlnorm(2); dlnorm(2, 0); dlnorm(2, 0, 1)[1] 0.156874[1] 0.156874[1] 0.156874[1] 0.156874[1] 0.1568744 rlnorm(): Random Sampling from Lognormal Distributions in R
Sample 1500 observations from the lognormal distribution with \(\tt{meanlog} = 1.8\) and \(\tt{sdlog} = 0.5\):
set.seed(123) # Line allows replication (use any number).
sample = rlnorm(1500, 1.8, 0.5)
hist(sample,
main = "Histogram of 1500 Observations from Lognormal Distribution
with Meanlog = 1.8 and SDlog = 0.5",
xlab = "x",
col = "deepskyblue", border = "white")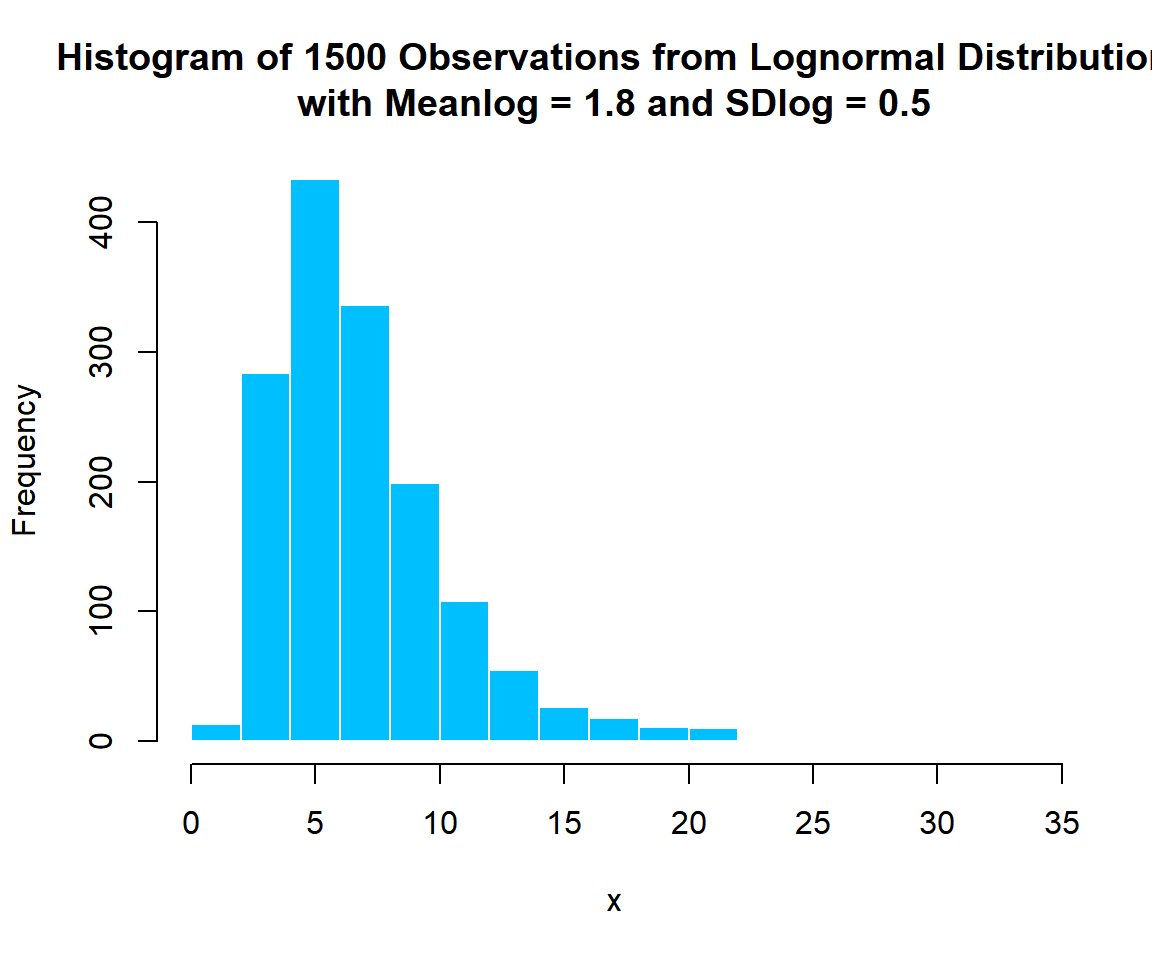
Histogram of Lognormal Distribution (1.8, 0.5) Random Sample in R
5 dlnorm(): Probability Density Function for Lognormal Distributions in R
Calculate the density at \(x = 4\), in the lognormal distribution with \(\tt{meanlog} = 0.75\) and \(\tt{sdlog} = 0.6\):
[1] 0.09472973x = seq(0, 12, 1/1000); y = dlnorm(x, 0.75, 0.6)
plot(x, y, type = "l",
xlim = c(0, 12), ylim = c(0, max(y)),
main = "Probability Density Function of Lognormal Distribution
with Mean = 0.75 and SDlog = 0.6",
xlab = "x", ylab = "Density",
lwd = 2, col = "blue")
# Add lines
segments(4, -1, 4, 0.09472973)
segments(-1, 0.09472973, 4, 0.09472973)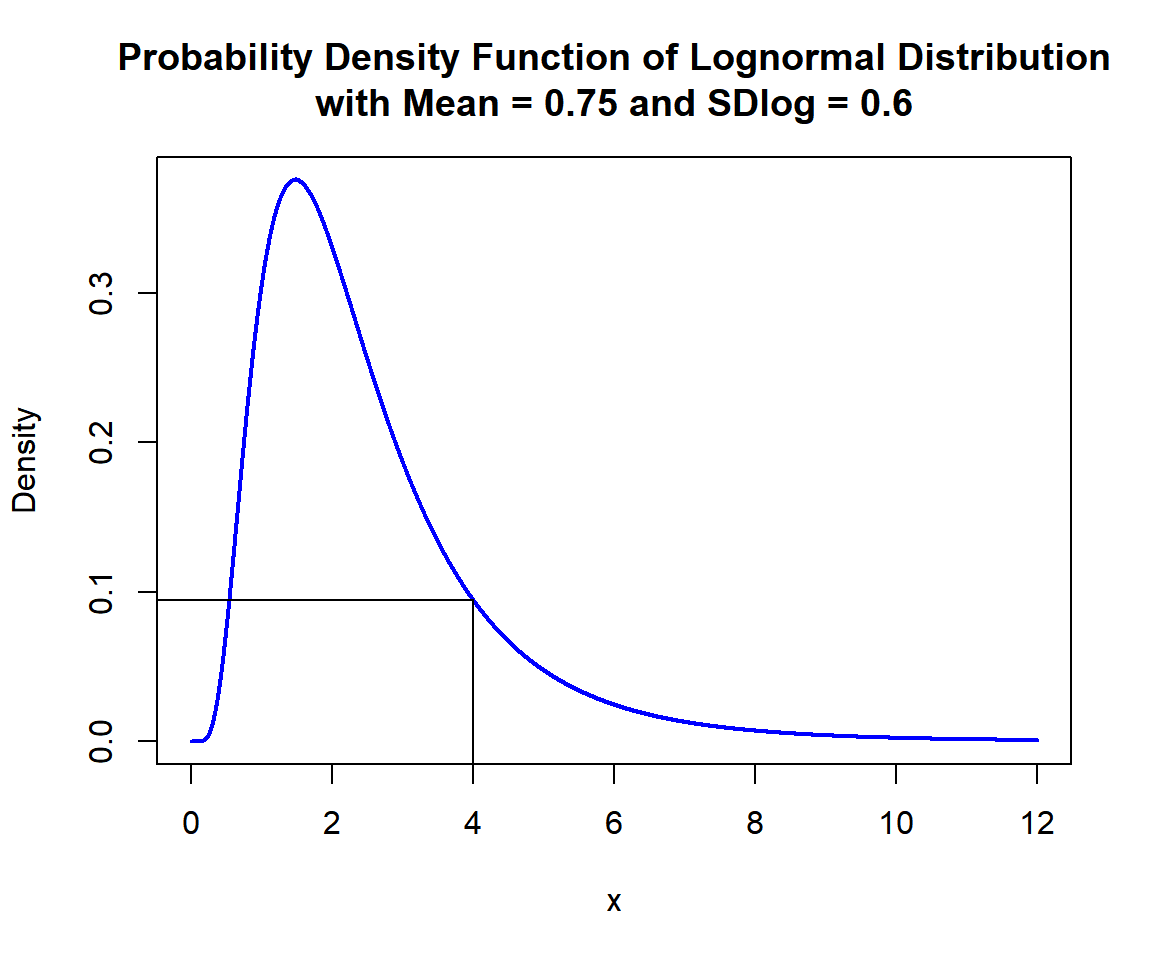
Probability Density Function (PDF) of Lognormal Distribution (0.75, 0.6) in R
6 plnorm(): Cumulative Distribution Function for Lognormal Distributions in R
Calculate the cumulative distribution at \(x = 2.5\), in the lognormal distribution with \(\tt{meanlog} = 0.8\) and \(\tt{sdlog} = 0.5\). That is, \(P(X \le 2.5)\):
[1] 0.5919568x = seq(0, 10, 1/1000); y = plnorm(x, 0.8, 0.5)
plot(x, y, type = "l",
xlim = c(0, 10), ylim = c(0,1),
main = "Cumulative Distribution Function of Lognormal Distribution
with Meanlog = 0.8 and SDlog = 0.5",
xlab = "x", ylab = "Cumulative Distribution",
lwd = 2, col = "blue")
# Add lines
segments(2.5, -1, 2.5, 0.5919568)
segments(-1, 0.5919568, 2.5, 0.5919568)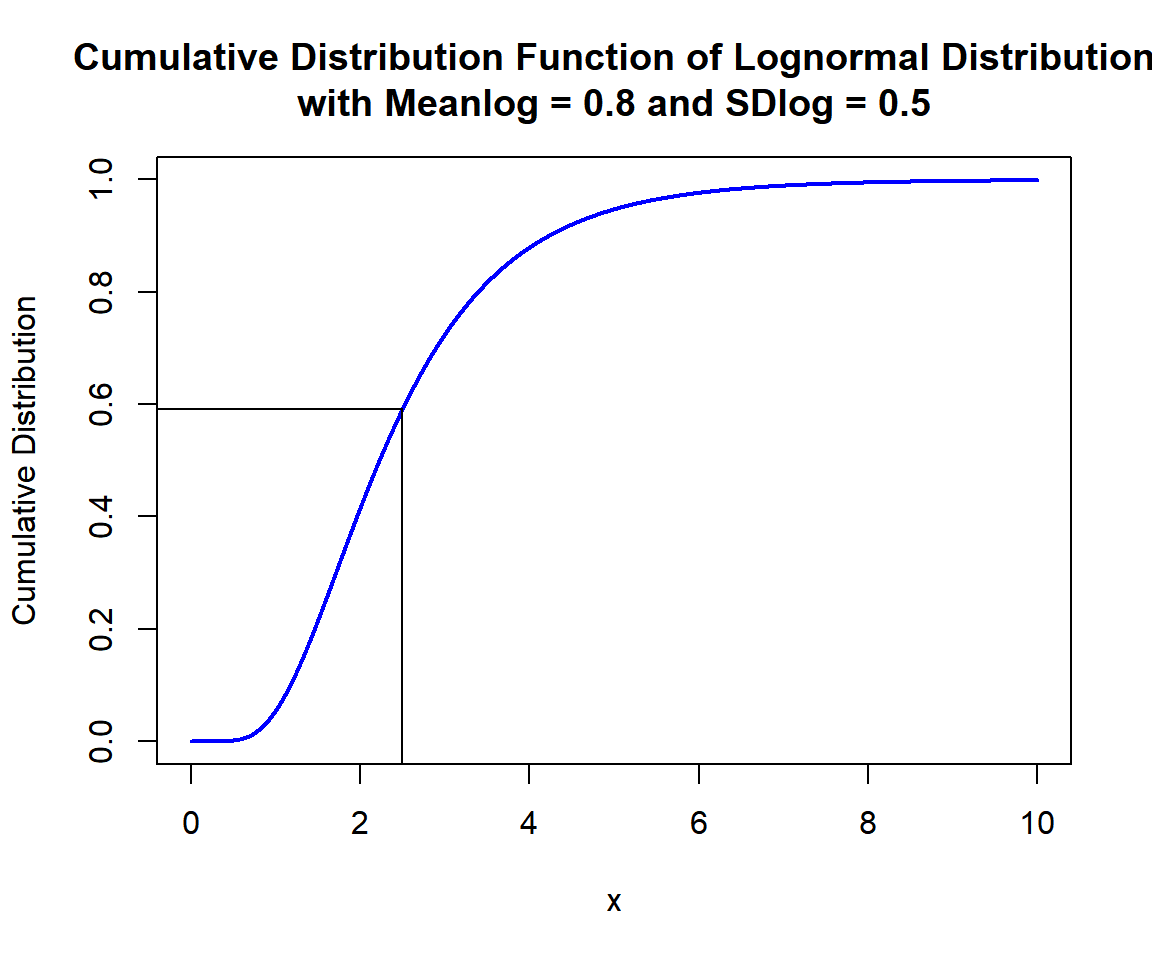
Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) of Lognormal Distribution (0.8, 0.5) in R
x = seq(0, 10, 1/1000); y = dlnorm(x, 0.8, 0.5)
plot(x, y, type = "l",
xlim = c(0, 10), ylim = c(0, max(y)),
main = "Probability Density Function of Lognormal Distribution
with Meanlog = 0.8 and SDlog = 0.5",
xlab = "x", ylab = "Density",
lwd = 2, col = "blue")
# Add shaded region and legend
point = 2.5
polygon(x = c(x[x <= point], point),
y = c(y[x <= point], 0),
col = "limegreen")
legend("topright", c("Area = 0.5919568"),
fill = c("limegreen"),
inset = 0.01)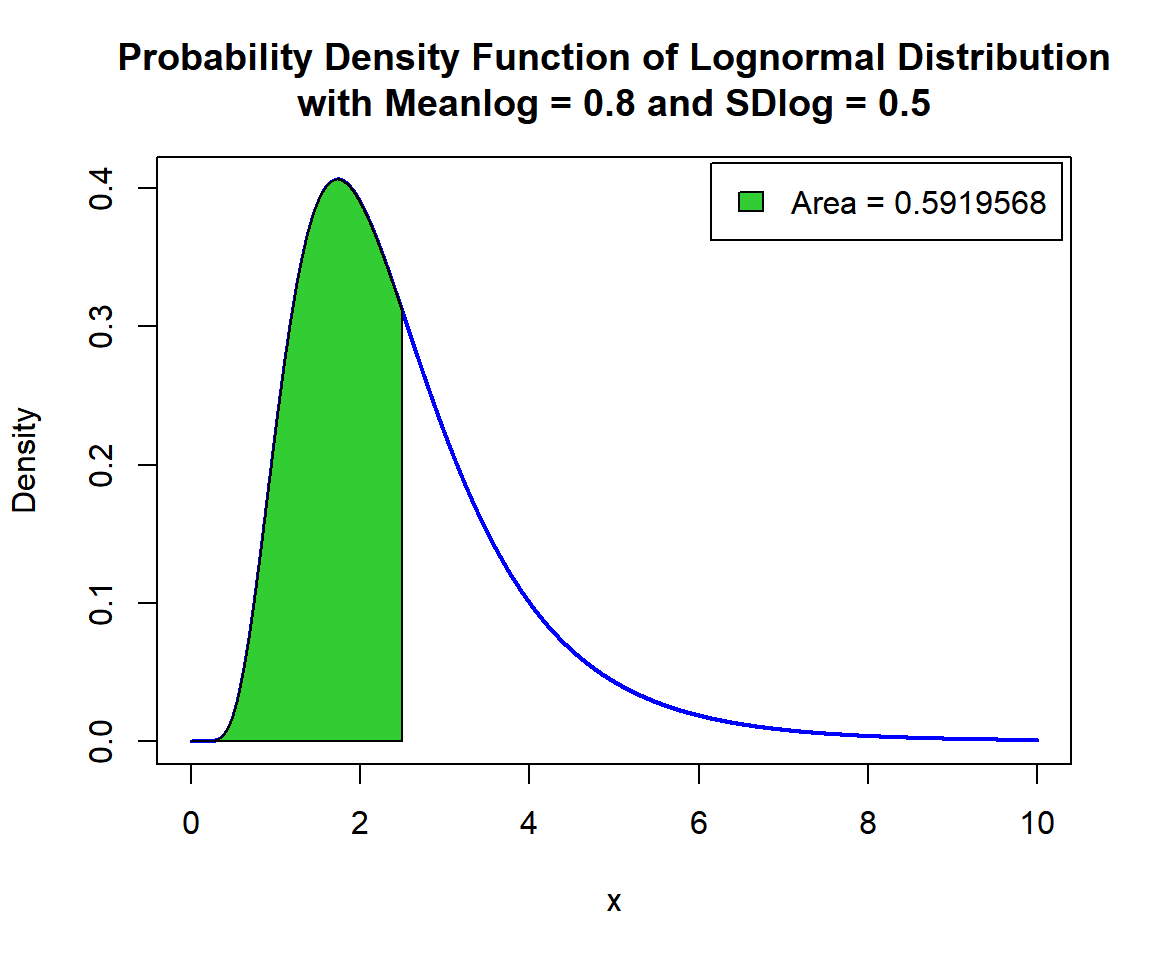
Shaded Probability Density Function (PDF) of Lognormal Distribution (0.8, 0.5) in R
For upper tail, at \(x = 2.5\), that is, \(P(X \ge 2.5) = 1 - P(X \le 2.5)\), set the "lower.tail" argument:
[1] 0.4080432x = seq(0, 10, 1/1000); y = dlnorm(x, 0.8, 0.5)
plot(x, y, type = "l",
xlim = c(0, 10), ylim = c(0, max(y)),
main = "Shaded Upper Region: Probability Density Function of
Lognormal Distribution with Meanlog = 0.8 and SDlog = 0.5",
xlab = "x", ylab = "Density",
lwd = 2, col = "blue")
# Add shaded region and legend
point = 2.5
polygon(x = c(point, x[x >= point]),
y = c(0, y[x >= point]),
col = "limegreen")
legend("topright", c("Area = 0.4080432"),
fill = c("limegreen"),
inset = 0.01)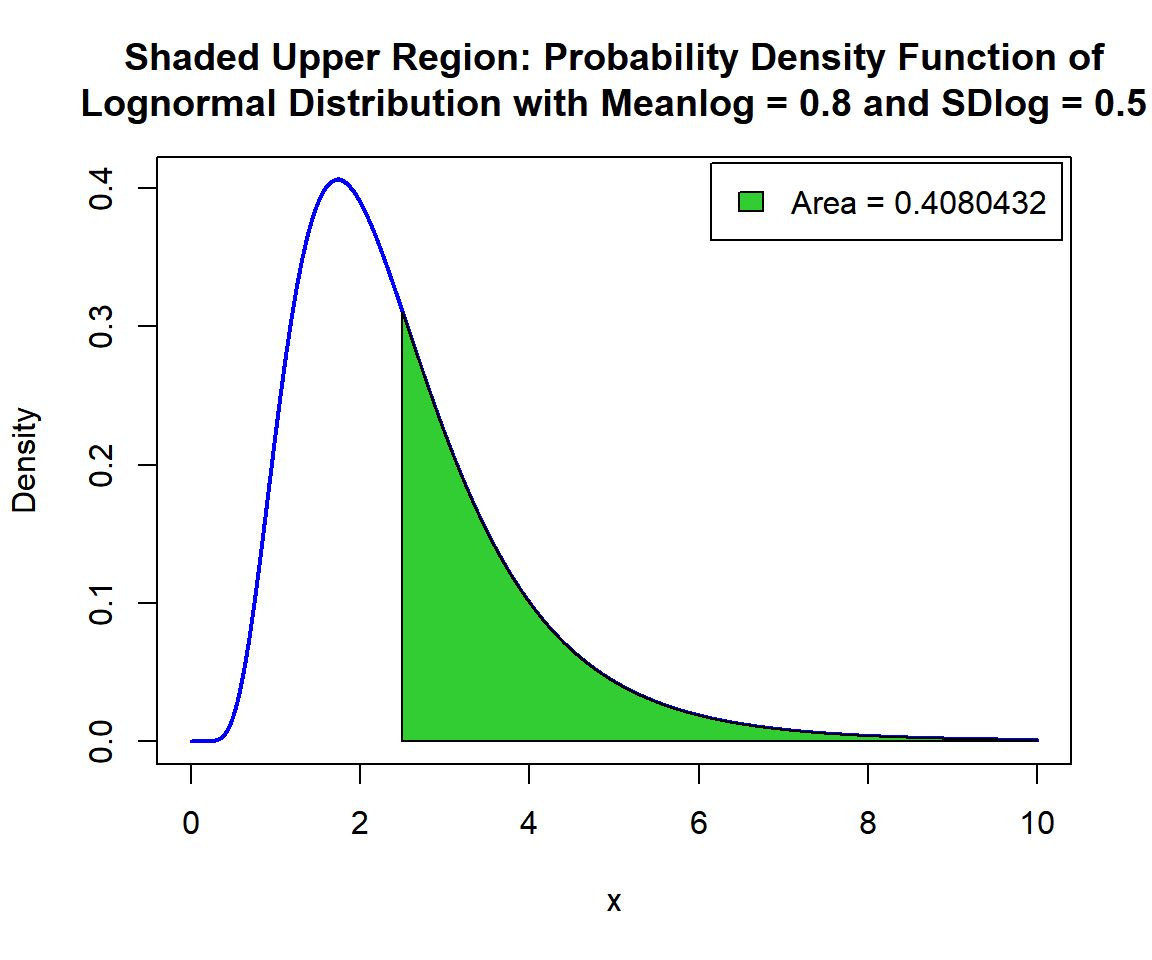
Shaded Upper Region: Probability Density Function (PDF) of Lognormal Distribution (0.8, 0.5) in R
7 qlnorm(): Derive Quantile for Lognormal Distributions in R
Derive the quantile for \(p = 0.9\), in the lognormal distribution with \(\tt{meanlog} = 1.5\) and \(\tt{sdlog} = 0.7\). That is, \(x\) such that, \(P(X \le x)=0.9\):
[1] 10.9911x = seq(0, 30, 1/1000); y = plnorm(x, 1.5, 0.7)
plot(x, y, type = "l",
xlim = c(0, 30), ylim = c(0,1),
main = "Cumulative Distribution Function of Lognormal Distribution
with Meanlog = 1.5 and SDlog = 0.7",
xlab = "x", ylab = "Cumulative Distribution",
lwd = 2, col = "blue")
# Add lines
segments(10.9911, -1, 10.9911, 0.9)
segments(-1, 0.9, 10.9911, 0.9)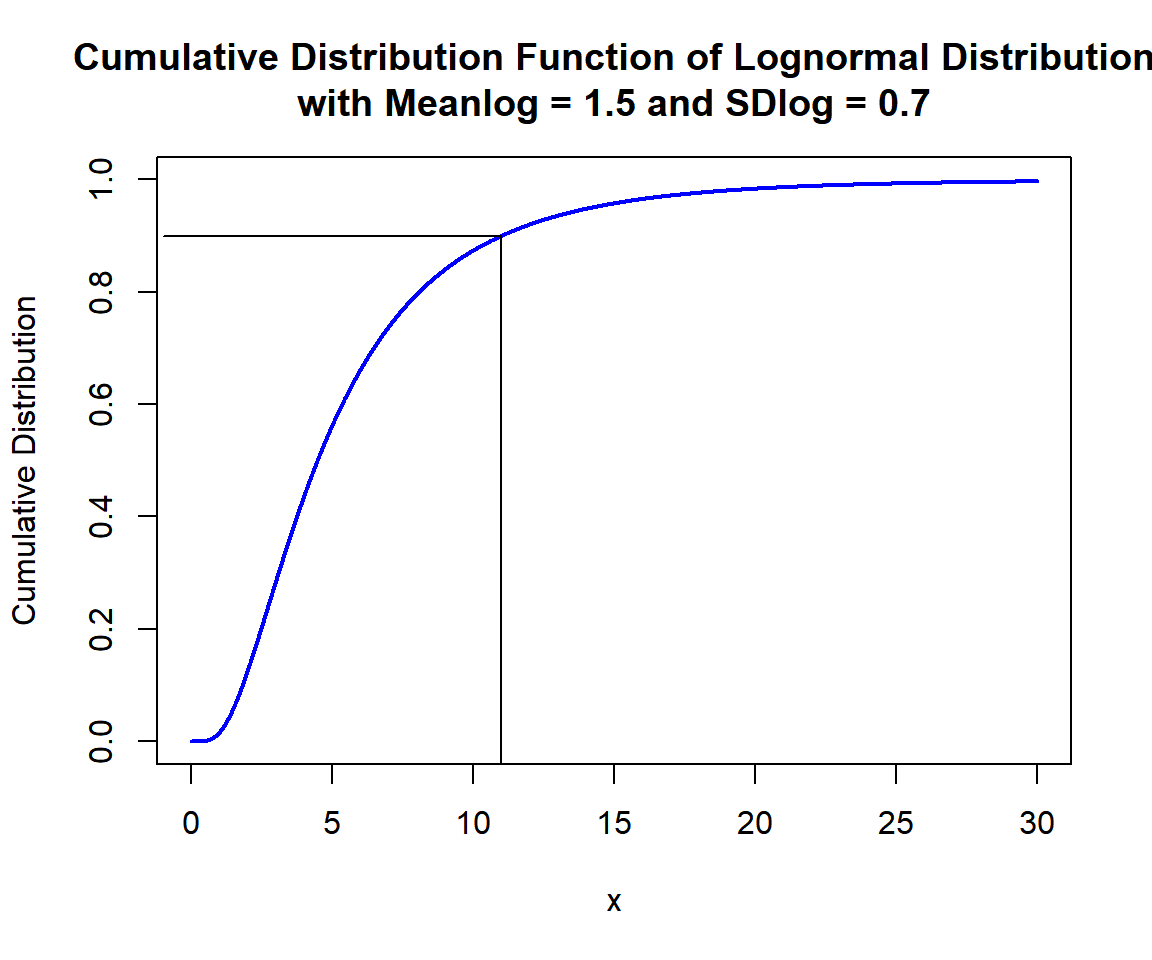
Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) of Lognormal Distribution (1.5, 0.7) in R
x = seq(0, 30, 1/1000); y = dlnorm(x, 1.5, 0.7)
plot(x, y, type = "l",
xlim = c(0, 30), ylim = c(0, max(y)),
main = "Probability Density Function of Lognormal Distribution
with Meanlog = 1.5 and SDlog = 0.7",
xlab = "x", ylab = "Density",
lwd = 2, col = "blue")
# Add shaded region and legend
point = 10.9911
polygon(x = c(x[x <= point], point),
y = c(y[x <= point], 0),
col = "limegreen")
legend("topright", c("Area = 0.9"),
fill = c("limegreen"),
inset = 0.01)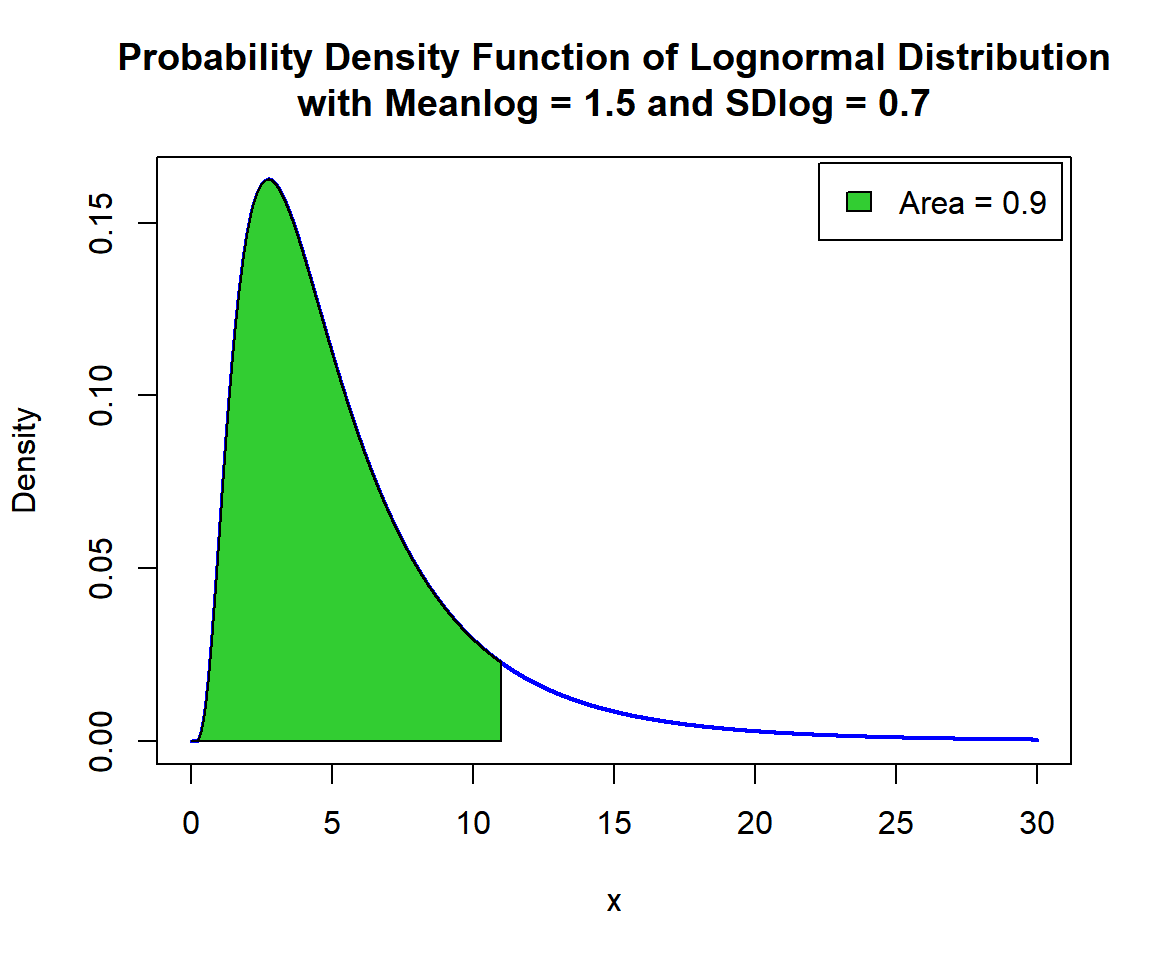
Shaded Probability Density Function (PDF) of Lognormal Distribution (1.5, 0.7) in R
For upper tail, for \(p = 0.1\), that is, \(x\) such that, \(P(X \ge x)=0.1\):
[1] 10.9911x = seq(0, 30, 1/1000); y = dlnorm(x, 1.5, 0.7)
plot(x, y, type = "l",
xlim = c(0, 30), ylim = c(0, max(y)),
main = "Shaded Upper Region: Probability Density Function of
Lognormal Distribution with Meanlog = 1.5 and SDlog = 0.7",
xlab = "x", ylab = "Density",
lwd = 2, col = "blue")
# Add shaded region and legend
point = 10.9911
polygon(x = c(point, x[x >= point]),
y = c(0, y[x >= point]),
col = "limegreen")
legend("topright", c("Area = 0.1"),
fill = c("limegreen"),
inset = 0.01)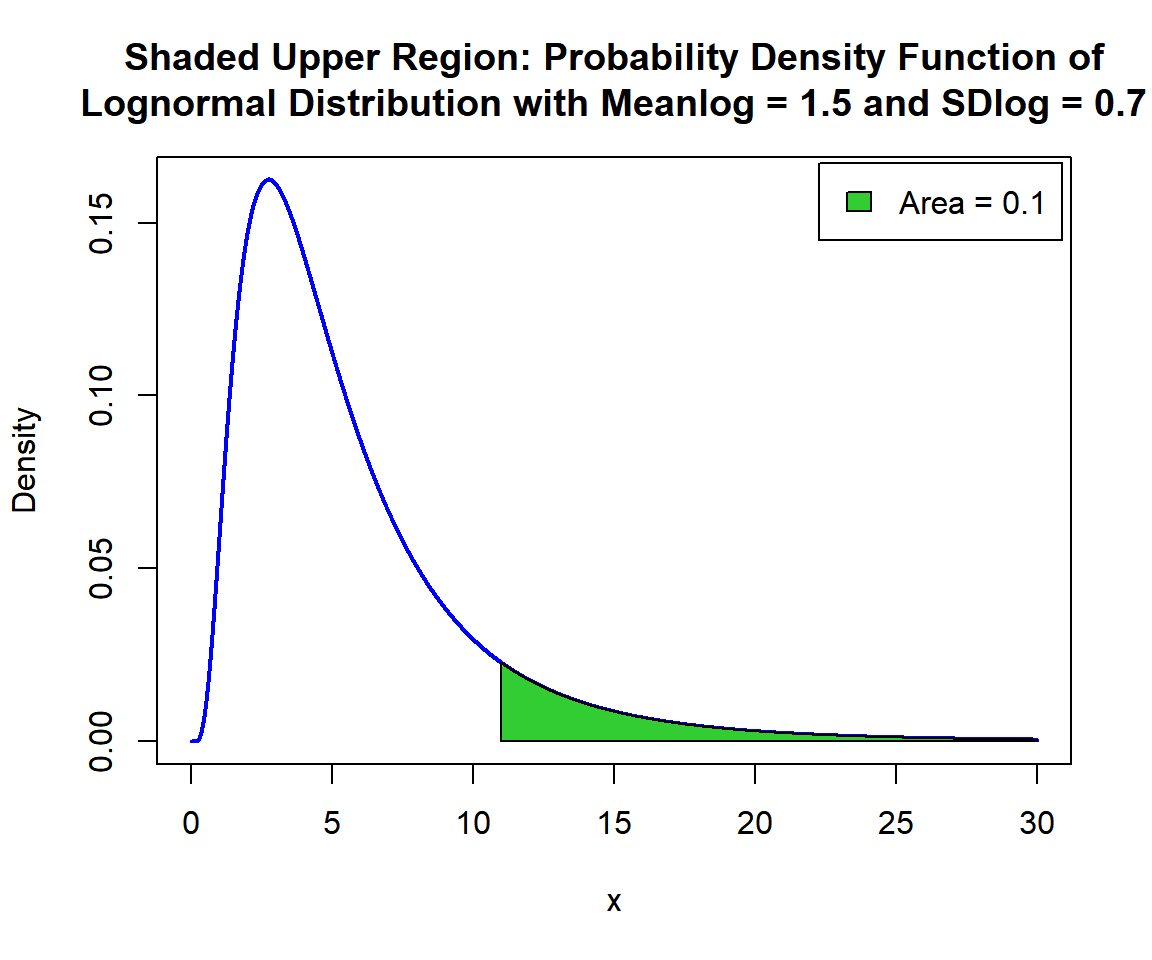
Shaded Upper Region: Probability Density Function (PDF) of Lognormal Distribution (1.5, 0.7) in R
The feedback form is a Google form but it does not collect any personal information.
Please click on the link below to go to the Google form.
Thank You!
Go to Feedback Form
Copyright © 2020 - 2024. All Rights Reserved by Stats Codes